
Harmonic Vibrational Analysis, frequency() and hessian()¶
For further discussion of vibrational and thermochemical analysis, see Sec. Vibrational and Thermochemical Analysis.
frequency() is the only command most users will ever
need to access directly to perform frequency calculations. Behind
the scenes, frequency() is a light wrapper over
hessian() that computes the Hessian then adds a
thermochemical analysis.
-
frequency(name[, molecule, return_wfn, func, mode, dertype, irrep])[source]¶ Function to compute harmonic vibrational frequencies.
Aliases: frequencies(), freq()
Returns: float – Total electronic energy in Hartrees.
Returns: (float, Wavefunction) – energy and wavefunction when return_wfn specified.
Parameters: - name (string) –
'scf'||'mp2'||'ci5'|| etc.First argument, usually unlabeled. Indicates the computational method to be applied to the system.
- molecule (molecule) –
h2o|| etc.The target molecule, if not the last molecule defined.
- return_wfn (boolean) –
'on'||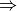
'off'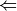
Indicate to additionally return the Wavefunction calculation result as the second element (after float energy) of a tuple. Arrays of frequencies and the Hessian can be accessed through the wavefunction.
- func (function) –
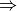
gradient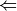 ||
|| energy||cbsIndicates the type of calculation to be performed on the molecule. The default dertype accesses
'gradient'or'energy', while'cbs'performs a multistage finite difference calculation. If a nested series of python functions is intended (see Function Intercalls), use keywordfreq_funcinstead offunc. - mode (string) –
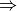
'continuous'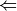 ||
|| 'sow'||'reap'For a finite difference of energies or gradients frequency, indicates whether the calculations required to complete the frequency are to be run in one file (
'continuous') or are to be farmed out in an embarrassingly parallel fashion ('sow'/'reap')/ For the latter, run an initial job with'sow'and follow instructions in its output file. For maximum flexibility,return_wfnis always on in'reap'mode. - dertype (dertype) –
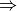
'hessian'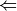 ||
|| 'gradient'||'energy'Indicates whether analytic (if available- they’re not), finite difference of gradients (if available) or finite difference of energies is to be performed.
- irrep (int or string) –
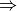
-1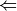 ||
|| 1||'b2'||'App'|| etc.Indicates which symmetry block (Cotton ordering) of vibrational frequencies to be computed.
1,'1', or'a1'represents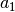 , requesting only the totally symmetric modes.
, requesting only the totally symmetric modes.
-1indicates a full frequency calculation.
Note
Analytic hessians are not available. Frequencies will proceed through finite differences according to availability of gradients or energies.
Examples: >>> # [1] Frequency calculation for all modes through highest available derivatives >>> frequency('ccsd')
>>> # [2] Frequency calculation for b2 modes through finite difference of gradients >>> # printing lowest mode frequency to screen and Hessian to output >>> E, wfn = frequencies('scf', dertype=1, irrep=4, return_wfn=True) >>> print wfn.frequencies().get(0, 0) >>> wfn.hessian().print_out()
>>> # [3] Frequency calculation at default conditions and Hessian reuse at STP >>> E, wfn = freq('mp2', return_wfn=True) >>> set t 273.15 >>> set p 100000 >>> thermo(wfn, wfn.frequencies())
- name (string) –
-
hessian(name[, molecule, return_wfn, func, dertype, irrep])[source]¶ Function complementary to
frequency(). Computes force constants, deciding analytic, finite difference of gradients, or finite difference of energies.Returns: Matrix – Total non-mass-weighted electronic Hessian in Hartrees/Bohr/Bohr. Returns: (Matrix, Wavefunction) – Hessian and wavefunction when return_wfn specified. Examples: >>> # [1] Frequency calculation without thermochemical analysis >>> hessian('mp3')
>>> # [2] Frequency calc w/o thermo analysis getting the Hessian >>> # in file, psi4.Matrix, and np.array forms >>> set hessian_write on >>> H, wfn = hessian('ccsd', return_wfn=True) >>> wfn.hessian().print_out() >>> np.array(H)