
Optimize¶
- optimize(name[, func, mode, dertype, molecule])[source]¶
Function to perform a geometry optimization.
Aliases : opt() Returns: (float) Total electronic energy of optimized structure in Hartrees. Psi variables: Note
Analytic gradients area available for all methods in the table below. Optimizations with other methods in the energy table proceed by finite differences.
name calls method scf Hartree–Fock (HF) or density functional theory (DFT) dcft density cumulant functional theory mp2 2nd-order Moller-Plesset perturbation theory (MP2) ccsd coupled cluster singles and doubles (CCSD) ccsd(t) CCSD with perturbative triples eom-ccsd equation of motion (EOM) CCSD Parameters: - name (string) –
'scf' || 'df-mp2' || 'ci5' || etc.
First argument, usually unlabeled. Indicates the computational method to be applied to the database. May be any valid argument to driver.energy().
- func (function) –
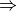 gradient
gradient 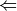 || energy || cbs
|| energy || cbsIndicates the type of calculation to be performed on the molecule. The default dertype accesses``’gradient’`` or 'energy', while 'cbs' performs a multistage finite difference calculation. If a nested series of python functions is intended (see Function Intercalls), use keyword opt_func instead of func.
- mode (string) –
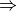 'continuous'
'continuous' 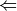 || 'sow' || 'reap'
|| 'sow' || 'reap'For a finite difference of energies optimization, indicates whether the calculations required to complete the optimization are to be run in one file ('continuous') or are to be farmed out in an embarrassingly parallel fashion ('sow'/'reap'). For the latter, run an initial job with 'sow' and follow instructions in its output file.
- dertype (dertype) –
'gradient' || 'energy'
Indicates whether analytic (if available) or finite difference optimization is to be performed.
- molecule (molecule) –
h2o || etc.
The target molecule, if not the last molecule defined.
Examples : >>> # [1] Analytic scf optimization >>> optimize('scf')
>>> # [2] Finite difference mp3 optimization >>> opt('mp3')
>>> # [3] Forced finite difference ccsd optimization >>> optimize('ccsd', dertype=1)
- name (string) –
For further discussion of geometry optimization, see Sec. Geometry Optimization.